AV PCT Configuration
AV PCT Configuration
Autonomous Vehicle Virtual Machine Configuration
The NVIDIA DRIVE? AGX system Autonomous Vehicle (AV) Partition Configuration Table (PCT) consists of server VMs, service VMs, and DRIVE AV Guest-OS (GOS) VM configurations.
PCT is divided according to the composition of the DRIVE AV GOS VM.
Single Linux GOS VM
Single QNX GOS VM
Dual QNX GOS VMs
Profile Makefile
The Profile Makefile is the file having definitions of PCT configuration. Each PCT have own Profile Makefiles.
Standard SDK/PDK package
Default Profile Makefile(profile.mk) is for Standard Package.
| PCT name | PCT | Profile Makefile for Standard build |
|---|---|---|
| Single Linux GOS VM | linux | profile.mk |
| Single QNX GOS VM | qnx | profile.mk |
| Dual QNX GOS VMs | dual-qnx | profile.mk |
The Profile Makefile is located at:
Single Linux GOS VM (linux PCT):
<top>/<NV_SDK_NAME_FOUNDATION>/platform-config/hardware/nvidia/platform/t23x/automotive/pct/drive_av/linux/profile.mkSingle QNX GOS VM (qnx PCT):
<top>/<NV_SDK_NAME_FOUNDATION>/platform-config/hardware/nvidia/platform/t23x/automotive/pct/drive_av/qnx/profile.mkDual QNX GOS VMs (dual-qnx PCT):
<top>/<NV_SDK_NAME_FOUNDATION>/platform-config/hardware/nvidia/platform/t23x/automotive/pct/drive_av/dual-qnx/profile.mkSafety SDK/PDK package
Safety build package need additional option (PCT varient option, -p) while bind to select different Profile Makefile for Safety Package. The Safety package has three types of profile configurations (PCT variant): prod, prod_debug, and prod_debug_extra. Especially prod_debug and prod_debug_extra PCT variant provide debug environment based on prod PCT variant.
| PCT name | PCT | PCT Variant | Profile Makefile for Safety build | Comment |
| Single Linux GOS VM | linux | N/A | N/A | linux PCT is not supported in Safety build. |
| Single QNX GOS VM | qnx | prod | profile_prod.mk | |
| prod_debug | profile_prod_debug.mk | Support communication to target over SSH/DHCP in GOS VM | ||
| prod_debug_extra | profile_prod_debug_extra.mk | Combined uart is enabled Servers/VM log available Support SSH/DHCP/NFS in GOS VM | ||
| Dual QNX GOS VMs | dual-qnx | prod | profile_prod.mk | |
| prod_debug | profile_prod_debug.mk | Support communication to target over SSH/DHCP in GOS VMs. | ||
| prod_debug_extra | profile_prod_debug_extra.mk | Combined uart is enabled Servers/VM log available Support SSH/DHCP/NFS in 1st GOS VMs |
These Profile Makefiles are located at:
Single QNX GOS VM (qnx PCT):
<top>/<NV_SDK_NAME_FOUNDATION>/platform-config/hardware/nvidia/platform/t23x/automotive/pct/drive_av/qnx/profile_prod.mk
<top>/<NV_SDK_NAME_FOUNDATION>/platform-config/hardware/nvidia/platform/t23x/automotive/pct/drive_av/qnx/profile_prod_debug.mk
<top>/<NV_SDK_NAME_FOUNDATION>/platform-config/hardware/nvidia/platform/t23x/automotive/pct/drive_av/qnx/profile_prod_debug_extra.mkDual QNX GOS VMs (dual-qnx PCT):
<top>/<NV_SDK_NAME_FOUNDATION>/platform-config/hardware/nvidia/platform/t23x/automotive/pct/drive_av/dual-qnx/profile_prod.mk
<top>/<NV_SDK_NAME_FOUNDATION>/platform-config/hardware/nvidia/platform/t23x/automotive/pct/drive_av/dual-qnx/profile_prod_debug.mk
<top>/<NV_SDK_NAME_FOUNDATION>/platform-config/hardware/nvidia/platform/t23x/automotive/pct/drive_av/dual-qnx/profile_prod_debug_extra.mkNote:
The prod_debug and prod_debug_extra PCTs are used for testing/debugging purposes. These PCTs use a different file package that must not be used as part of the software stack in a running car.
Supported Platform and CPU allocation
The following tables list the supported combination of PCT, platform, and SDK/PDK package.
The CPUs column indicates the number of CPUs assigned to the guest VM and to the server VMs, respectively.
Supported Platform and Board Name
| Official Name | Platform | Board Name | 940/694-BOARD-SKU-REV | Comment |
| DRIVE Orin | p3663 |
|
| |
|
| Emmc Size increased to 64GB compared to 32GB on p3663-a01 | ||
|
| MAX96981B display serializer with DSC on top of p3663-01-a02 boards | ||
| DRIVE AGX Orin Devkit | p3710 |
|
| ct02 is for chip sku TA985SA/TA979SA support. |
|
|
| ||
|
| |||
|
| |||
|
| GMSL out interconnect board delta compared to DisplayPort Interconnect Board on p3710-10-a03 | ||
|
| GMSL out interconnect board delta compared to DisplayPort Interconnect Board on p3710-10-a04 | ||
|
| GMSL out interconnect board delta compared to DisplayPort Interconnect Board on p3710-10-s05 |
Note:
Board names with suffix -ct02 have 8 CPU cores. Normally, Orin have 12 CPU cores.
Standard SDK/PDK package
| Orin type | PCT | CPUs: GOS0(+GOS1)+Servers |
|---|---|---|
| 12 cpu cores | qnx / dual-qnx / linux | 11(+1 shared cpu with GOS0)+1 |
| 8 cpu cores | qnx / linux | 7+1 |
Safety SDK/PDK package
| Orin type | PCT | PCT Variant | CPUs: GOS0(+GOS1)+Servers |
|---|---|---|---|
| 12 cpu cores | qnx / dual-qnx | prod / prod_debug / prod_debug_extra | 11(+1 shared cpu with GOS0)+1 |
| 8 cpu cores | qnx | prod / prod_debug / prod_debug_extra | 7+1 |
The example guest_config.h shows the mapping between the guest OS and services as well as their allocations.
Use Cases of NDAS/ECO, eMMC/UFS Secondary boot device
Depending on the use cases, storage configuration and peripheral assignment are different.
The following table lists the supported use cases with platforms.
| Use cases | First boot device +Secondary boot device | Platforms |
| Driving ECU (NDAS) | QSPI+eMMC | p3663 / p3710 |
| EcoSystem/General (ECO) | QSPI+eMMC | p3663 / p3710 |
| QSPI+UFS | p3710 | |
| Recoder (REC) | QSPI+eMMC | p4024 |
Enable DRAM ECC for DRIVE AV PCT
DRAM ECC feature can be enabled for DRIVE AV PCT by modifying Profile Makefiles. Below needs to be added in profile makefiles to enable DRAM ECC.
ENABLE_DRAM_ECC := yRefer to Profile Makefile to figure out which profile makefile needs to be modified.
Note:
DRAM ECC feature is enabled for QNX safety PCTs by default.
Disable FSI for DRIVE AV Linux PCTs
FSI can be disabled for DRIVE AV Linux PCTs by modifying Profile Makefiles. Below needs to be added in profile makefiles to disable FSI.
ENABLE_FSI := nRefer to Profile Makefile to figure out which profile makefile needs to be modified.
Note:
FSI is enabled for Drive AV Linux PCTs by default.
ECID read access on Guest VMs
Read access to ECID can be provided to Guest VMs by configuring below in guest_config.h for a VM in PCT settings.
can_read_ecid_hash = 1ECID is considered as a solution for customer to get a unique ID of the platform from customer's application.
Note:
ECID read access is disabled for Drive AV PCTs for all VMs by default.
Bind Options
A bind process creates a hypervisor image that combines DTB/IFS/KERNEL of server VMs, Hypervisor kernel, and PCT.
Syntax:
# for standard package
$ cd drive-foundation/
# for safety package
$ cd drive-foundation-safety/
$ ./make/bind_partitions [-b <board_name>] <pct> [-u <use_case>] [-r <storage_config>] [-p <pct_variant>] [options]Example of Standard Linux PCT + ECO(QSPI+UFS) use case on DRIVE AGX Orin Devkit:
bind_partitions -b p3710-10-a01 linuxNote:
The default configuration of p3710-1* is Standard ECO QSPI+UFS. If you want ECO QSPI+eMMC boot, use the '-u eco' option.
Example of Standard QNX PCT + NDAS use case on DRIVE Orin:
bind_partitions -b p3663-a01 qnx -u ndasSupported Bind Options
The following tables list the supported bind options.
Bind options for Standard package
Note:
Get full <board_name> from Supported platform and Board Name
| Use cases | bind cmd | -b <board_name> | <pct> | -u <use_case> (default) | -r <storage_config> (default) | Comment |
| ECO | bind_partitions |
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
| p3710 default secondary boot device is UFS(QSPI+UFS). | ||
| NDAS | bind_partitions |
|
|
|
| With BASE storage config option(-r base), UFS device is disabled. |
|
|
| dual-qnx support only NDAS storage config. | |||
| REC | bind_partitions |
|
| N/A | N/A |
Bind options for Safety package
| Use cases | bind cmd | -b <board_name> | <pct> | -u <use_case> (default) | -r <storage_config> (default) | -p <pct_variant> |
| ECO | bind_partitions |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
| NDAS | bind_partitions |
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
Bind options for power profile
| Platforms | Standard or Safety | Power Profile (default) |
| p3663 | Standard and Safety |
|
| p3710 | Standard |
|
| Safety |
| |
| p4024 | Standard |
|
Bind options for SOC ID for C2C in GOS-DT
| Platforms | SOC ID for C2C in GOS-DT | Comments |
| p3663 / p3710 / p4024 | -s <SOC_ID:1~4294967295> | Specify SOC ID in GOS-DTand rebuild GOS device tree |
When the <SOC_ID> argument is specified with the -s option, SOC_IDENTIFICATION_VALUE is defined and
the <SOC_ID> value will be set for soc_id in GOS-DT property.
#ifdef SOC_IDENTIFICATION_VALUE
soc_id = <SOC_IDENTIFICATION_VALUE>;
#else
soc_id = <1>;
#endifAV PCT Input/Output Resource Assignment
The ownership of input/output peripherals is divided between the guest OS and the service VMs.
The following table details the type of access the guest OS or service VMs have for each I/O peripheral.
QNX and Linux PCT Standard Package Profile
| Resources | Resources Shared? | Update VM | Guest OS |
|---|---|---|---|
| DRAM | Yes | 512MB | ~30 GB(32GB RAM) / ~13 GB(16GB RAM) |
| iGPU | Yes | N/A | Virtual |
| DLA | No | N/A | DLA0, DLA1 |
| PVA | No | N/A | PVA0, PVA1 |
| NvEnc / OFA | No | N/A | Assigned |
| VIC | No | N/A | Assigned |
| Display | No | N/A | Assigned |
| QSPI | Yes | Virtual | N/A |
| eMMC0 (32/64GB) | Yes | Virtual | Virtual |
| UFS (265GB) | Yes | Virtual | Virtual |
| 1G ethernet | No | N/A | Assigned |
| SPI Master | No | N/A | Assigned |
| SPI Slave | No | N/A | Assigned (Only for linux PCT) |
| RCE (ISP, VI, MIPICAL, NVCSI, CSI lanes) | No | N/A | Assigned |
| I2C Master | No | N/A | Assigned |
| GPIO | No | N/A | Assigned |
| Tegra CAN | No | N/A | Assigned |
| NVDEC | No | N/A | Assigned |
| NVJPG | No | N/A | Assigned |
| 10G Ethernet | No | N/A | Assigned |
| Pcie Controller EP+RP for C2C | No | N/A | Assigned (Only for P3710) |
| Pcie Controller , UART for Wifi/BT | No | N/A | Assigned |
| SE Engine | Yes | Virtual | Virtual |
| I2S, A2B/codec driver | No | N/A | Assigned |
| dGPU | No | N/A | Assigned |
Dual-QNX PCT Standard Package Profile
| Resources | Resources Shared? | Update VM | Guest OS | Guest OS1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DRAM | Yes | 512MB | ~29 GB(32GB RAM) / ~12 GB(16GB RAM) | 1 GB |
| iGPU | Yes | N/A | Virtual | N/A |
| DLA | No | N/A | DLA0, DLA1 | N/A |
| PVA | No | N/A | PVA0, PVA1 | N/A |
| NvEnc / OFA | No | N/A | Assigned | N/A |
| VIC | No | N/A | Assigned | N/A |
| Display | No | N/A | Assigned | N/A |
| QSPI | Yes | Virtual | N/A | N/A |
| eMMC0 (32/64GB) | Yes | Virtual | Virtual | Virtual |
| UFS (265GB) | Yes | Virtual | Virtual | N/A |
| 1G ethernet | No | N/A | Assigned | N/A |
| SPI Master | No | N/A | Assigned | N/A |
| SPI Slave | No | N/A | Assigned (Only for linux PCT) | N/A |
| RCE (ISP, VI, MIPICAL, NVCSI, CSI lanes) | No | N/A | Assigned | N/A |
| I2C Master | No | N/A | Assigned | N/A |
| GPIO | No | N/A | Assigned | N/A |
| Tegra CAN | No | N/A | Assigned | N/A |
| NVDEC | No | N/A | Assigned | N/A |
| NVJPG | No | N/A | Assigned | N/A |
| 10G Ethernet | No | N/A | Assigned | N/A |
| Pcie Controller EP+RP for C2C | No | N/A | Assigned (Only for P3710) | N/A |
| Pcie Controller , UART for Wifi/BT | No | N/A | N/A | Assigned |
| SE Engine | Yes | Virtual | Virtual | Virtual |
| I2S, A2B/codec driver | No | N/A | Assigned | N/A |
| dGPU | No | N/A | Assigned | N/A |
Note:
Regarding SDRAM usage, the amount of physical memory available for each virtual machine for virtual RAM is determined by a fixed (base) amount plus a dynamic (growth) amount. The value for the fixed amount is read directly from the PCT. The value for the dynamic amount is based on the amount of memory remaining after the fixed allocation and subsequently assigned to each virtual machine based on a per-VM growth factor. Higher growth factors result in a higher proportion of memory allocated to a virtual machine.
IVC Mapping
Inter-virtual machine Communication (IVC) facilitates data exchange between two virtual machines over shared memory.
The platform_config.h shows IVC queues between VMs, services, and servers in the AV PCT.
Mempool Mapping
The platform_config.h shows mempool mapping between VMs, services, and servers in the AV PCT.
Note:
Each VM/service Guest ID (GID) using in IVC/Mempool mapping is define in the following code snippet.
<top>/<NV_SDK_NAME_FOUNDATION>/virtualization/make/t23x/server-partitions.mk
ifeq (,$(NR_VM))
NR_VM := 0
VM_GID = $(shell echo $$(($(NR_VM))))
VM_GID_MASK = $(shell echo $$((1 << ($(NR_VM)))))
INC_NR_VM = $(shell echo $$(($(NR_VM)+1)))
ifeq (y,$(ENABLE_GUEST0_VM))
LOCAL_FLAGS += -DGID_GUEST0_VM=$(VM_GID)
LOCAL_FLAGS += -DGOS0_VM=$(VM_GID_MASK)
GID_GUEST0_VM := $(VM_GID)
NR_VM := $(INC_NR_VM)
endif
ifeq (y,$(ENABLE_GUEST1_VM))
LOCAL_FLAGS += -DGID_GUEST1_VM=$(VM_GID)
LOCAL_FLAGS += -DGOS1_VM=$(VM_GID_MASK)
GID_GUEST1_VM := $(VM_GID)
NR_VM := $(INC_NR_VM)
endif
ifeq (y,$(ENABLE_UPDATE_VM))
LOCAL_FLAGS += -DGID_UPDATE=$(VM_GID)
LOCAL_FLAGS += -DUPDATE_VM=$(VM_GID_MASK)
GID_UPDATE := $(VM_GID)
NR_VM := $(INC_NR_VM)
endif
endif
ID := 0
cont-files :=
GID = $(shell echo $$(($(ID)+$(NR_VM))))
GID_MASK = $(shell echo $$((1 << ($(ID)+$(NR_VM)))))
INC_ID = $(shell echo $$(($(ID)+1)))Gpio Ownership
The guest_gpio_ownership.h shows gpio ownership to a guest OS.
I2C Ownership
The guest_i2c_ownership.h shows i2c ownership to a guest OS.
Drive AV Storage Configuration
In the PCT, there are three configuration files that implements the three level partitioning concept:
global_storage.cfg
This is the “root” of the definition hierarchy.
It defines the top level partitioning, and contains partitions that are present regardless of which boot chain is active
It is referred to as the First level(level-1) partition table storage config file.
boot_chain_storage.cfg file like mentioned after “sub_cfg_file=” in Level-1 partitions.
Contains partitions that will be unique to each of the boot chains.
It is referred to as the Second level(level-2) partition table storage config file.
qnx_gos0_storage.cfg file like mentioned after “sub_cfg_file=” in Level-2 partitions.
Contains partitions that will be unique to each of Level-2 container partitions.
It is referred to as the Third level(level-3) partition table storage config file.
Three-Level Partitioning
The following diagram gives an example of a three level partition layout and 3 level partition tables.

The eMMC A chain: It consists of all eMMC partitions assigned to all virtual machines in the Partition Configuration Table (PCT). All content in this chain can be overwritten by the OTA application.
The eMMC B chain: This is the recovery chain. The target boots in this chain when the OTA application is about to update other boot chains.
The QSPI C chain: This is the recovery chain to boot with only QSPI. The target boots in this chain when the OTA application is about to update other boot chains.
Persistent partitions for all virtual machines: The data partitions that are NOT updated by the OTA application. Data over these partitions remain consistent over multiple OTA cycles.
Inspecting the global_storage.cfg (level-1) you will notice it refers to boot_chain_storage.cfg as a “sub_config” file. This elevates the boot_chain_storage_qspi.cfg to be level-2.
...
[partition]
name=A_qspi_chain
...
sub_cfg_file=boot_chain_storage.cfg
[partition]
name=B_qspi_chain
...
sub_cfg_file=boot_chain_storage.cfg
[partition]
name=C_qspi_chain
...
sub_cfg_file=boot_chain_c_storage.cfgSimilarly, inspecting the boot_chain_storage.cfg (level-2) you will notice it refers to the OS storage config file. This elevates the OS storage config file to be level-3.
[partition]
name=qnx-gos0
...
sub_cfg_file=qnx_gos0_storage.cfg
Since level-3 is derived from Level-2, its content will be duplicated in each of the boot chains (A & B).
Level-1 Storage Configuration Structure
General structure of this file is:
device 1 information
partition 1.1 information
....
partition 1.n information
device 2 information
partition 2.1 information
....
partition 2.n information
etc.
Device information highlighted by this application note are:
linux_name=/dev/block/3270000.spi - name of peripheral device
size=0x940000 - total size of storage device
Note:
For Level-2 & Level-3 configurations, the size is not the total size of the device, but it is the allowed size of storage device for that level, as defined in previous level.
Partition information highlighted by this application note are:
name=bct - logical name of the partition
size=0x80000 - size of the partition
Partitions that utilize the “sub_cfg_file” are container partitions. These partitions share the same space with partitions in “sub_cfg_file”. The size attribute specifies the allowed space the next level can use on the device.
For the QSPI storage, the allowed space for Level-2 & Level-3 is specified by the size
[partition]
name=A_qspi_chain
size=0x940000
[partition]
name=B_qspi_chain
size=0x940000Since Level-2 and Level-3 also allocate storage on eMMC/UFS, the limit on how much eMMC/UFS storage can be allocated is defined here :
[partition]
name=A_emmc_chain
size=EMMC_BOOTCHAIN_SIZE
[partition]
name=B_emmc_chain
size=EMMC_BOOTCHAIN_SIZE
name=A_ufs_chain
size=UFS_BOOTCHAIN_SIZE
name=A_ufs_chain
size=UFS_BOOTCHAIN_SIZELevel-1 Partition Table
The information about of all partitions in Level-1, as been allocated on both QSPI & eMMC/UFS, are stored in a partition table file
[partition]
name=pt
size=0x80000This partition CANNOT be updated when the DU process is done. This table is common to Chain A & Chain B, so both chains' future updates must preserve the content of Level-1 partitions. If not, DU process will fail.
Level-2 and Level-3 Storage Configuration Structure
These follow the same rules as Level-1, i.e. General structure of this file is:
device 1 information
partition 1.1 information
....
partition 1.n information
device 2 information
partition 2.1 information
....
partition 2.m information
Each level can specify partitions on QSPI & eMMC/UFS storage devices. The “device” record size is the max allowed storage space for that level, not the full size. Both levels will affect the content of Chain A and Chain B.
Customizing the Drive AV Storage Configuration
Configuration Files
The default storage layout QSPI and eMMC/UFS are as shown in their respective tables below (Refer storage-layout). Users can customize the storage layout for mass storage partitions on the target by modifying the configuration files. After the configuration files are updated, the target must be flashed again.
For Single Linux GOS VM PCT:
Storage configuration files
<top>/<NV_SDK_NAME_FOUNDATION>/platform-config/hardware/nvidia/platform/t23x/automotive/pct/drive_av/linux/GOS0 DTB for virtual storage nodes
<top>/<NV_SDK_NAME_LINUX>/kernel/source/hardware/nvidia/platform/t23x/automotive/kernel-dts/common/linux/storage/tegra234-common-storage-linux-gos.dtsiFor Single QNX GOS VM PCT:
Storage configuration files
<top>/<NV_SDK_NAME_FOUNDATION>/platform-config/hardware/nvidia/platform/t23x/automotive/pct/drive_av/qnx/GOS0 DTB for virtual storage nodes
<top>/<NV_SDK_NAME_QNX>/bsp/device-tree/hardware/nvidia/platform/t23x/automotive/kernel-dts/common/qnx/storage/tegra234-common-driveav-storage-gos0.dtsiFor Dual QNX GOS VMs PCT :
Storage configuration files:
<top>/<NV_SDK_NAME_FOUNDATION>/platform-config/hardware/nvidia/platform/t23x/automotive/pct/drive_av/dual-qnxGOS0 DTB for virtual storage nodes
<top>/<NV_SDK_NAME_QNX>/bsp/device-tree/hardware/nvidia/platform/t23x/automotive/kernel-dts/common/qnx/storage/tegra234-common-driveav-storage-gos0.dtsiGOS1 DTB for virtual storage nodes
<top>/<NV_SDK_NAME_QNX>/bsp/device-tree/hardware/nvidia/platform/t23x/automotive/kernel-dts/common/qnx/storage/tegra234-common-driveav-storage-gos1.dtsiVirtual Partitions
Partitions tare allocated to the QNX/Linux Virtual Machine(VM) and are physically managed by Virtual Storage Controller(VSC) server VM. These partitions are defined to be virtual partitions.
This is being discussed in PDK manual, Storage Server / Virtualized Storage in NVIDIA DRIVE OS 6.0 Linux PDK Developer Guide or NVIDIA DRIVE OS 6.0 QNX Development Guide.
These partitions are accessible to the VM(s) via inter VM communications channels called Inter-VM-Channel(IVC) which is a bi-directional short command oriented interface, and memory-pool which is a shared memory buffer. These are only accessible by the QNX/Linux VM and the VSC.
There are two files to modify:
<top>/<NV_SDK_NAME_FOUNDATION>/platform-config/hardware/nvidia/platform/t23x/automotive/pct/drive_av/platform_ivc_config.h
Allocate unused IVC number and define a new constant named:
#if defined(PLATFORM_<BOARD NAME>)
#define GOS0_VSC_Q_<#> <#>
#endifIVC number can be added up to 255.
At the end of same file, allocate an unused memory pool id, and define a new constant
#if defined(PLATFORM_<BOARD NAME>)
#define GOS0_VSC_M_<##> <##>
#endif<top>/<NV_SDK_NAME_FOUNDATION>/platform-config/hardware/nvidia/platform/t23x/automotive/pct/drive_av/platform_config.h
Within the block of defining <VM><VM>Q<#> , locate the pre-processor associated with the storage device type you are adding a partition to. Example:
#if defined (ENABLE_VSC_EMMC_VIRT)
#if defined (ENABLE_VSC_UFS_VIRT)
#ifdef ENABLE_VSC_QSPI0_VIRT
Optional :
#ifdef ENABLE_VSC_QSPI1_VIRT
#ifdef ENABLE_VSC_SDMMC1_VIRTAdd the following line to that block
#if defined(PLATFORM_<BOARD NAME>)
/* <partition name> */
[GOS0_VSC_Q_<#>] = { .peers = {GID_GUEST0_VM, GID_VSC_SERVER}, .nframes = 16, .frame_size = SZ_128 },
#endifWithin the block of defining <VM><VM>M<#> , locate the pre-processor associated with the storage device type you are adding a partition to. Example:
#f defined (ENABLE_VSC_EMMC_VIRT)
#if defined (ENABLE_VSC_UFS_VIRT)
#ifdef ENABLE_VSC_QSPI0_VIRT
Optional :
#ifdef ENABLE_VSC_QSPI1_VIRT
#ifdef ENABLE_VSC_SDMMC1_VIRTAdd the following line to that block
#if defined(PLATFORM_<BOARD NAME>)
/* <partition name> */
[GOS0_VSC_M_<##>] = { .peers = {GID_GUEST0_VM, GID_VSC_SERVER}, .nframes = 16, .frame_size = SZ_128 },
#endifThe new IVC number added in previous step as <#>, and the new mempool number added in the previous step as <##>, need to be added in two configurations files:
In the storage configuration file where the new partition was added the following new attributes need to be added.
The last four string(Two HEX values) in virtual_storage_ivc_ch are the hexadecimal representation of the memory pool and IVC channel (<mempool><IVC>).
partition_attribute=<GID_GUEST0_VM+1>
virtual_storage_ivc_ch=0x8<GID_VSC_SERVER>00<HEX##><HEX#>The 32-bit virtual_storage_ivc_ch value can be broken down as follows:
| Bit | Description |
| [31] | Is Virtual Storage Flag [virt = 1, non-virt = 0] |
| [30:24] | Storage Server ID [int value from 0-0x7F] |
| [23] | Shared Partition Flag [shared = 1, exclusive = 0] |
| [22:17] | RESERVED |
| [16] | Read only flag [RO =1, RW = 0] |
| [15:8] | Mempool ID [int value from 0-0xFF] |
| [0:7] | IVC Queue ID [int value from 0-0xFF] |
The presence of the partitions to be used by the QNX VM is defined in its device tree via the following file:
<top>/<NV_SDK_NAME_QNX>/bsp/device-tree/hardware/nvidia/platform/t23x/automotive/kernel-dts/common/qnx/storage/tegra234-common-driveav-storage-gos0.dtsi
Each partition has a node describing it. example:
tegra_virt_storage0 { <<== required name, number is incrementing
compatible = "nvidia,tegra-hv-storage"; <<== required field, as is
status = "okay"; <<== required field, as is
instance = <0>; <<== instance id 0..n for each device type. This will determine node name in QNX File System
ivc = <&tegra_hv #>; <<== ivc number used <#> in decimal
mempool = <##>; <<== mempool number used <##> in decimal
device-type = "vblk_mnand"; <<== one of "vblk_mnand", "vblk_sifs", "vblk_ufs"
partition-name = "usr-fs"; <<== partition name as defined earlier in storage configuration files.
read-only; <<== optional token for read-only partition. omit if read/write
};Constraints
QNX OS expects the partition layout in a specific order. Refer to the chapter Mass Storage Partitions Configuration in NVIDIA DRIVE OS 6.0 Linux PDK Developer Guide or NVIDIA DRIVE OS 6.0 QNX Development Guide.
Partition sizes should be 256K aligned.
IVC queue number should be smaller than 256.
Drive AV Storage Layout
First Level Partition Table(L1PT) Layout
The global_storage.cfg file defines the total size of storage devices, boot chain container partitions and persistent partitions of guest VMs.
The first level configuration has the following layout for the ECO QSPI+eMMC use case:
| Device | Partition | Size (Hex bytes) | IVC Value (Depends on VSC Server GID) | Mandatory | Customizable | Purpose |
| QSPI - 0 size (0x4000000) | bct (BR-BCT) | 0x80000 | 0x8<GID_VSC_SERVER>002560 | Yes | No | Holds Board configuration information. |
| pt (PT_1) | 0x80000 | 0x8<GID_VSC_SERVER>002661 | Yes | No | L1 Partition Table | |
| C_qspi_chain | 0x2C00000 | 0x8<GID_VSC_SERVER>802C66 | Yes | No | L1 container partitions for holding C chain on qspi | |
| bad-page (PBL) | 0x80000 | N/A | No | No | For DRAM ECC | |
| A_qspi_chain | 0x940000 | 0x8<GID_VSC_SERVER>802762 | Yes | No | L1 container partitions for holding A chain on qspi | |
| B_qspi_chain | 0x940000 | 0x8<GID_VSC_SERVER>802863 | Yes | No | L1 container partitions for holding B chain on qspi | |
| EMMC - 3 size (0xE8FC00000 for 64GB) (0x747C00000 for 32GB) | A_emmc_chain | 0x72D080000 for 64GB 0x38D0C0000 for 32GB | 0x8<GID_VSC_SERVER>802964 | Yes | Yes | L1 container partitions for holding A chain on emmc |
| B_emmc_chain | 0x72D080000 for 64GB 0x38D0C0000 for 32GB | 0x8<GID_VSC_SERVER>802A65 | Yes | Yes | L1 container partitions for holding B chain on emmc | |
| gos0-shared-pers | 0x10000000 | 0x8<GID_VSC_SERVER>0036ED | No | Yes | Persistent shared user partition of GOS0 | |
| pers-ota | 0x10000000 | 0x8<GID_VSC_SERVER>00245F | Yes | No | Persistent Storage for Update VM | |
| UFS - 0 size (0x3A00000000) | A_ufs_chain | 0xD00000000 | 0x8<GID_VSC_SERVER>802D70 | No | Yes | L1 container partitions for holding A chain on ufs |
| B_ufs_chain | 0xD00000000 | 0x8<GID_VSC_SERVER>802E71 | No | Yes | L1 container partitions for holding B chain on ufs | |
| gos0-ufs | 0x1D00000000 | 0x8<GID_VSC_SERVER>003FF7 | No | Yes | User persistent data of GOS0 | |
| gos0-demo-ufs (only for linux) | 0x280000000 | 0x8<GID_VSC_SERVER>0040F8 | No | Yes | To demonstrate Encrypted File System feature |
The first level configuration has the following layout for the ECO QSPI+UFS use case:
| Device | Partition | Size (Hex bytes) | IVC Value (Depends on VSC Server GID) | Mandatory | Customizable | Purpose |
| QSPI - 0 size (0x4000000) | bct (BR-BCT) | 0x80000 | 0x8<GID_VSC_SERVER>002560 | Yes | No | Holds Board configuration information. |
| pt( PT_1) | 0x80000 | 0x8<GID_VSC_SERVER>002661 | Yes | No | L1 Partition Table | |
| C_qspi_chain | 0x2C00000 | 0x8<GID_VSC_SERVER>802C66 | Yes | No | L1 container partitions for holding C chain on qspi | |
| bad-page( PBL) | 0x80000 | N/A | No | No | For DRAM ECC | |
| A_qspi_chain | 0x940000 | 0x8<GID_VSC_SERVER>802762 | Yes | No | L1 container partitions for holding A chain on qspi | |
| B_qspi_chain | 0x940000 | 0x8<GID_VSC_SERVER>802863 | Yes | No | L1 container partitions for holding B chain on qspi | |
| EMMC - 3 size (0xE8FC00000 for 64GB) (0x747C00000 for 32GB) | A_emmc_chain | 0x72D080000 for 64GB 0x38D0C0000 for 32GB | 0x8<GID_VSC_SERVER>802964 | Yes | Yes | L1 container partitions for holding A chain on emmc |
| B_emmc_chain | 0x72D080000 for 64GB 0x38D0C0000 for 32GB | 0x8<GID_VSC_SERVER>802A65 | Yes | Yes | L1 container partitions for holding B chain on emmc | |
| UFS - 0 size (0x3A00000000) | A_ufs_chain | 0xD00000000 | 0x8<GID_VSC_SERVER>802D70 | Yes | Yes | L1 container partitions for holding A chain on ufs |
| B_ufs_chain | 0xD00000000 | 0x8<GID_VSC_SERVER>802E71 | Yes | Yes | L1 container partitions for holding B chain on ufs | |
| gos0-shared-pers | 0x10000000 | 0x8<GID_VSC_SERVER>0036ED | No | Yes | Persistent shared user partition of GOS0 | |
| pers-ota | 0x10000000 | 0x8<GID_VSC_SERVER>00245F | Yes | No | Persistent Storage for Update VM | |
| gos0-ufs | 0x1D00000000 | 0x8<GID_VSC_SERVER>003FF7 | No | Yes | User persistent data of GOS0 | |
| gos0-demo-ufs (only for linux) | 0x280000000 | 0x8<GID_VSC_SERVER>0040F8 | No | Yes | To demonstrate Encrypted File System feature |
The first level configuration has the following layout for the NDAS use case:
| Device | Partition | Size (Hex bytes) | IVC Value (Depends on VSC Server GID) | Mandatory | Customizable | Purpose |
| QSPI - 0 size (0x4000000) | bct (BR-BCT) | 0x80000 | 0x8<GID_VSC_SERVER>002560 | Yes | No | Holds Board configuration information. |
| pt (PT_1) | 0x80000 | 0x8<GID_VSC_SERVER>002661 | Yes | No | L1 Partition Table | |
| C_qspi_chain | 0x2C00000 | 0x8<GID_VSC_SERVER>802C66 | Yes | No | L1 container partitions for holding C chain on qspi | |
| bad-page (PBL) | 0x80000 | N/A | No | No | For DRAM ECC | |
| A_qspi_chain | 0x940000 | 0x8<GID_VSC_SERVER>802762 | Yes | No | L1 container partitions for holding A chain on qspi | |
| B_qspi_chain | 0x940000 | 0x8<GID_VSC_SERVER>802863 | Yes | No | L1 container partitions for holding B chain on qspi | |
| EMMC - 3 size (0x747C00000) | A_emmc_chain | 0x25BEC0000 | 0x8<GID_VSC_SERVER>802964 | Yes | No | L1 container partitions for holding A chain on emmc |
| B_emmc_chain | 0x25BEC0000 | 0x8<GID_VSC_SERVER>802A65 | Yes | No | L1 container partitions for holding B chain on emmc | |
| gos0-misc-pers | 0x6600000 | 0x8<GID_VSC_SERVER>0035EC | Yes | No | ||
| gos0-ota-pers | 0x10000000 | 0x8<GID_VSC_SERVER>0036ED | Yes | No | ||
| guest0-shadow-pers | 0x66600000 | 0x8<GID_VSC_SERVER>0037EE | Yes | No | ||
| gos0-m-stream-pers | 0x40000000 | 0x8<GID_VSC_SERVER>0039F0 | Yes | No | ||
| gos0-p-map-pers | 0x40000000 | 0x8<GID_VSC_SERVER>003AF1 | Yes | No | ||
| gos0-s-logger-pers | 0x60000000 | 0x8<GID_VSC_SERVER>003BF2 | Yes | No | ||
| gos0-sar-pers | 0x13300000 | 0x8<GID_VSC_SERVER>003CF3 | Yes | No | ||
| gos0-dlb-pers | 0x4000000 | 0x8<GID_VSC_SERVER>003DF4 | Yes | No | ||
| gos1-config-pers | 0xA00000 (Only for dual-qnx) | 0x8<GID_VSC_SERVER>802F72 | Yes | No | ||
| pers-ota | 0x10000000 | 0x8<GID_VSC_SERVER>00245F | Yes | No | Persistent Storage for Update VM | |
| UFS - 0 UFS device is only for HIGH storage config size (0x1D00000000) | A_ufs_chain | 0xC80000000 | 0x8<GID_VSC_SERVER>802D70 | No | Yes | L1 container partitions for holding A chain on ufs |
| B_ufs_chain | 0xC80000000 | 0x8<GID_VSC_SERVER>802E71 | No | Yes | L1 container partitions for holding B chain on ufs | |
| gos0-m-cache-ufs | 0x200000000 | 0x8<GID_VSC_SERVER>0040F8 | No | Yes | ||
| gos0-sar-ufs | 0xC0000000 | 0x8<GID_VSC_SERVER>0041F9 | No | Yes | ||
| gos0-edr-ufs | 0xC0000000 | 0x8<GID_VSC_SERVER>0042FA | No | Yes |
2nd Level Partition Table(L2PT) Layout
l2pt_qspi QSPI Chain-A/B Layout
QSPI partitions include bct files, bootloaders, and firmware binaries.
The storage layout for QSPI is as follows:
| QSPI Partition Name | Size (in KBytes) | Mandatory | customizable | Purpose |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PT_2(pt) | 256 | Yes | No | L2 Partition Table |
| mb1-bootloader | 256 | Yes | No | Primary Copy of MB1 Bootloader |
| PSC-BL1 (psc-bl) | 256 | Yes | No | PSC firmware |
| MB1-BCT (mb1-bct) | 256 | Yes | No | BCT for MB1 |
| MemBct (mem-bct) | 256 | Yes | No | BCT for memory configuration |
| IST_UCode(ccplex-ist-ucode) | 256 | Yes | No | IST ucode |
| MB2+MB2-BCT (mb2-bootloader) | 512 | Yes | No | MB2 |
| SPE_FW (spe-fw) | 512 | Yes | No | Sensor Processing Engine firmware |
| PSC_FW (psc-fw) | 768 | Yes | No | Firmware for PSC |
| MCE (mts-mce) | 256 | Yes | No | Firmware for cpu cores |
| BPMP_FW(bpmp-fw) | 1536 | Yes | No | Firmware for BPMP |
| SC7-RF | 256 | Yes | No | BPMP SC7 resume firmware |
| PSC-RF | 256 | Yes | No | PSC resume firmware |
| MB2-RF | 256 | Yes | No | CPU resume firmware |
| BPMP_FW_DTB (bpmp-fw-dtb) | 512 | Yes | No | DT for BPMP |
| RCE_FW (rce-fw) | 1024 | Yes | No | RCE firmware image |
| nvdec-fw | 512 | Yes | No | NVDEC firmware |
| Key IST uCode (ist-ucode) | 256 | Yes | No | IST key |
| IST_BPMP (bpmp-ist) | 256 | Yes | No | IST bpmp |
| IST_ICT (ist-config) | 256 | Yes | No | IST ICT |
Note:
Chain B (same as Chain A) partitions are not included in the above table.
l2pt_qspi_c QSPI Chain-C Layout
| QSPI Partition Name | Size (in KBytes) | Mandatory | customizable | Purpose |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PT_2(pt) | 256 | Yes | No | L2 Partition Table |
| mb1-bootloader | 256 | Yes | No | Primary Copy of MB1 Bootloader |
| PSC-BL1 (psc-bl) | 256 | Yes | No | PSC firmware |
| MB1-BCT (mb1-bct) | 256 | Yes | No | BCT for MB1 |
| MemBct (mem-bct) | 256 | Yes | No | BCT for memory configuration |
| MB2+MB2-BCT (mb2-bootloader) | 512 | Yes | No | MB2 |
| SPE_FW (spe-fw) | 512 | Yes | No | Sensor Processing Engine firmware |
| PSC_FW (psc-fw) | 768 | Yes | No | Firmware for PSC |
| MCE (mts-mce) | 256 | Yes | No | Firmware for cpu cores |
| BPMP_FW( bpmp-fw) | 1536 | Yes | No | Firmware for BPMP |
| BPMP_FW_DTB (bpmp-fw-dtb) | 512 | Yes | No | DT for BPMP |
| cpu-bootloader | 512 | Yes | No | QB |
| secure-os | 4096 | Yes | No | TOS |
| fsi-fw | 6144 | Yes | No | FSI FW |
| RCE_FW (rce-fw) | 1024 | Yes | No | RCE firmware image |
| kernel (HV image) | 6656 | Yes | No | HV kernel + server VMs + PCT |
| guest-linux-chain_c (Linux GOS VM 3LPT) | 13312 | Yes | No | Linux kernel/initramfs/DT/GPT/rootfs |
| qnx-update-chain_c (IFS/DT of Drive Update VM L3PT) | 6144 | Yes | No | Update VM QNX primary IFS image and DT |
emmc-part eMMC and UFS partitions
The eMMC/UFS device connected to Orin is partitioned logically to enable each VM to have its own root file system or to store user data. Each VM is assigned a dedicated user partition on eMMC/UFS and might have secondary user partitions for storing additional data. The eMMC/UFS device on board is shared between the VMs.
The eMMC/UFS Storage Chain A/B for QNX PCT ECO use case:
| Partition Name | Size (in MBytes) | Mandatory | customizable | Purpose | Partition exist in |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ist-testimg | 1280 | Yes | No | IST test image | eMMC |
| ist-runtimeinfo | 0.25 | Yes | No | IST runtime information | eMMC |
| ist-resultdata | 200 | Yes | No | IST result data | eMMC |
| gr-ist | 0.25 | Yes | No | gr blob support | eMMC |
| oist-tst-vtr | 128 | Yes | No | Runtime IST test vector | eMMC (QSPI+eMMC boot) UFS (QSPI+UFS boot) |
| cpu-bootloader | 0.5 | Yes | No | QB | eMMC (QSPI+eMMC boot) UFS (QSPI+UFS boot) |
| secure-os | 4 | Yes | No | TOS | eMMC (QSPI+eMMC boot) UFS (QSPI+UFS boot) |
| adsp-fw | 2 (only for standard) | Yes | No | For Audio | eMMC (QSPI+eMMC boot) UFS (QSPI+UFS boot) |
| fsi-fw | 6 | Yes | No | FSI FW | eMMC (QSPI+eMMC boot) UFS (QSPI+UFS boot) |
| xusb-fw | 0.25 | Yes | No | XUSB FW | eMMC (QSPI+eMMC boot) UFS (QSPI+UFS boot) |
| kernel (HV image) | 10 | Yes | No | HV kernel + server VMs + PCT | eMMC (QSPI+eMMC boot) UFS (QSPI+UFS boot) |
| gos0-debug_overlay (GOS0 Debug Overlay) | 128 (only for safety) | Yes | No | Debug overly for safety images only | eMMC (QSPI+eMMC boot) UFS (QSPI+UFS boot) |
| qnx-gos0 (IFS/DT for GOS0 L3PT) | 30 | Yes | No | GOS0 QNX primary IFS image and DT | eMMC (QSPI+eMMC boot) UFS (QSPI+UFS boot) |
| gos0-ifs2 (Secondary IFS) | 500 | Yes | No | QNX secondary IFS image | eMMC (QSPI+eMMC boot) UFS (QSPI+UFS boot) |
| usr-fs (GOS EFS1) | 2560 (for standard) 2030 (for safety) | Yes | No | Guest OS rootfs | eMMC (QSPI+eMMC boot) UFS (QSPI+UFS boot) |
| gos0-efs2 (GOS EFS2) | 7680 | Yes | No | Guest OS extended file system #2 | eMMC (QSPI+eMMC boot) UFS (QSPI+UFS boot) |
| gos0-efs3 (GOS EFS3) | 1536 (for 32GB eMMC) 16384 (for 64GB eMMC or QSPI+UFS) | Yes | No | Guest OS extended file system #3 | eMMC (QSPI+eMMC boot) UFS (QSPI+UFS boot) |
| qnx-update (IFS/DT of Drive Update VM L3PT) | 24 | Yes | No | Update VM QNX primary IFS image and DT | eMMC (QSPI+eMMC boot) UFS (QSPI+UFS boot) |
| qnx-update-fs | 128 | Yes | No | Filesystem of Update VM QNX | eMMC (QSPI+eMMC boot) UFS (QSPI+UFS boot) |
| gos0-compute-bits-ufs (compute-bits) | 4096 | Yes | No | For CuDNN TRT | UFS |
Where:
/dev/vblk_*denotes the enumeration for a given partition from guest OS or service VM. The partitions must be formatted before use.IFS: Early boot partition with minimal file system that contains the kernel.
EFS: QNX root file system, additional file system demonstration bits, sample applications, and data.
All partitions present in
boot_chain_storage.cfgare part of the OTA update.All sub-configuration files that are in the
boot_chain_storage.cfgare also part of the OTA update.
The eMMC/UFS Storage Chain A/B for Linux PCT ECO use case:
| Partition Name | Size (in MBytes) | Mandatory | customizable | Purpose | Partition exist in |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ist-testimg | 1280 | Yes | No | IST test image | eMMC |
| ist-runtimeinfo | 0.25 | Yes | No | IST runtime information | eMMC |
| ist-resultdata | 200 | Yes | No | IST result data | eMMC |
| gr-ist | 0.25 | Yes | No | gr blob support | eMMC |
| gos0-crashlogs | 1 | No | Yes | To store Oops logs | eMMC |
| cpu-bootloader | 0.5 | Yes | No | QB | eMMC (QSPI+eMMC boot) UFS (QSPI+UFS boot) |
| secure-os | 4 | Yes | No | TOS | eMMC (QSPI+eMMC boot) UFS (QSPI+UFS boot) |
| adsp-fw | 2 | Yes | No | For Audio | eMMC (QSPI+eMMC boot) UFS (QSPI+UFS boot) |
| fsi-fw | 6 | Yes | No | FSI FW | eMMC (QSPI+eMMC boot) UFS (QSPI+UFS boot) |
| xusb-fw | 0.25 | Yes | No | XUSB FW | eMMC (QSPI+eMMC boot) UFS (QSPI+UFS boot) |
| dce-fw | 9 | Yes | No | DCE FW | eMMC (QSPI+eMMC boot) UFS (QSPI+UFS boot) |
| kernel (HV image) | 10 | Yes | No | HV kernel + server VMs + PCT | eMMC (QSPI+eMMC boot) UFS (QSPI+UFS boot) |
| guest-linux (Linux GOS VM 3LPT) | 12818 (for 32GB eMMC) 27666 (for 64GB eMMC or QSPI+UFS) | Yes | No | Linux kernel/initramfs/DT/GPT/rootfs | eMMC (QSPI+eMMC boot) UFS (QSPI+UFS boot) |
| qnx-update (IFS/DT of Drive Update VM L3PT) | 24 | Yes | No | Update VM QNX primary IFS image and DT | eMMC (QSPI+eMMC boot) UFS (QSPI+UFS boot) |
| qnx-update-fs | 128 | Yes | No | Filesystem of Update VM QNX | eMMC (QSPI+eMMC boot) UFS (QSPI+UFS boot) |
| gos0-compute-bits-ufs (compute-bits) | 4096 | Yes | No | For CuDNN TRT | UFS |
The eMMC/UFS Storage Chain A/B for QNX (qnx/dual-qnx) PCT NDAS use case:
| Partition Name | Size (in MBytes) | Mandatory | customizable | Purpose | Partition exist in |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ist-testimg | 1280 | Yes | No | IST test image | eMMC |
| ist-runtimeinfo | 0.25 | Yes | No | IST runtime information | eMMC |
| ist-resultdata | 200 | Yes | No | IST result data | eMMC |
| gr-ist | 0.25 | Yes | No | gr blob support | eMMC |
| oist-tst-vtr | 128 | Yes | No | Runtime IST test vector | eMMC |
| cpu-bootloader | 0.5 | Yes | No | QB | eMMC |
| secure-os | 4 | Yes | No | TOS | eMMC |
| adsp-fw | 2 (only for standard) | Yes | No | For Audio | eMMC |
| fsi-fw | 6 | Yes | No | FSI FW | eMMC |
| xusb-fw | 0.25 | Yes | No | XUSB FW | eMMC |
| kernel (HV image) | 10 | Yes | No | HV kernel + server VMs + PCT | eMMC |
| gos0-debug_overlay (GOS0 Debug Overlay) | 128 (only for safety) | Yes | No | Debug overly for safety images only | eMMC |
| qnx-gos0 (IFS/DT for GOS0 L3PT) | 30 | Yes | No | GOS0 QNX primary IFS image | eMMC |
| gos0-ifs2( GOS0 Secondary IFS) | 500 | Yes | No | GOS0 QNX secondary IFS image | eMMC |
| usr-fs (GOS0 Root-FS) | 2030 | Yes | No | GOS0 root file system | eMMC |
| gos0-av-rootfs (GOS0 AV Root-FS) | 4096 | Yes | No | Automotive applications rootfs | eMMC |
| gos1-debug_overlay (GOS1 Debug Overlay) | 128 (only for dual-qnx safety) | Yes | No | Debug overly for safety images only | eMMC |
| qnx-gos1 (IFS/DT for GOS1 L3PT) | 30 (only for dual-qnx) | Yes | No | GOS1 QNX primary IFS image | eMMC |
| gos1-ifs2 (GOS1 Secondary IFS) | 98 (only for dual-qnx) | Yes | No | GOS1 QNX secondary IFS image | eMMC |
| gos1-av( GOS1 AV-FS) | 256 (only for dual-qnx) | Yes | No | Guest OS1 av file system | eMMC |
| qnx-update (IFS/DT of Drive Update VM L3PT) | 24 | Yes | No | Update VM QNX primary IFS image and DT | eMMC |
| qnx-update-fs | 128 | Yes | No | Filesystem of Update VM QNX | eMMC |
| gos0-compute-bits-ufs (compute-bits) | 4096 (only for HIGH config) | Yes | No | For CuDNN TRT | UFS |
| gos0-usr-data-ufs (UserData UFS) | 8192 (only for HIGH config) | Yes | No | GOS0 user data | UFS |
The eMMC/UFS Storage Chain A/B for Linux PCT NDAS use case:
| Partition Name | Size (in MBytes) | Mandatory | customizable | Purpose | Partition exist in |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ist-testimg | 1280 | Yes | No | IST test image | eMMC |
| ist-runtimeinfo | 0.25 | Yes | No | IST runtime information | eMMC |
| ist-resultdata | 200 | Yes | No | IST result data | eMMC |
| gr-ist | 0.25 | Yes | No | gr blob support | eMMC |
| cpu-bootloader | 0.5 | Yes | No | QB | eMMC |
| secure-os | 4 | Yes | No | TOS | eMMC |
| adsp-fw | 2 | Yes | No | For Audio | eMMC |
| fsi-fw | 6 | Yes | No | FSI FW | eMMC |
| xusb-fw | 0.25 | Yes | No | XUSB FW | eMMC |
| dce-fw | 9 | Yes | No | DCE FW | eMMC |
| kernel (HV image) | 10 | Yes | No | HV kernel + server VMs + PCT | eMMC |
| guest-linux (Linux GOS VM 3LPT) | 3456 | Yes | No | Linux kernel/initramfs/DT/GPT/rootfs | eMMC |
| gos0-av-rootfs (GOS0 AV Root-FS) | 4096 | Yes | No | Automotive applications rootfs | eMMC |
| qnx-update (IFS/DT of Drive Update VM L3PT) | 24 | Yes | No | Update VM QNX primary IFS image and DT | eMMC |
| qnx-update-fs | 128 | Yes | No | Filesystem of Update VM QNX | eMMC |
| gos0-compute-bits-ufs (compute-bits) | 4096 (only for HIGH config) | Yes | No | For CuDNN TRT | UFS |
| gos0-usr-data-ufs (UserData UFS) | 8192 (only for HIGH config) | Yes | No | GOS0 user data | UFS |
GPT L3 Support
GUID based partition table support is added for GOS at L3 level. With this feature the partitions in L3 under GPT can be independently updated including the partition table.
To add a GPT partition at 3rd level(L3), a container partition needs to be added at 2nd level(L2). Level 2 container partition holds the GPT primary and backup partition layout along with the actual partition contents.
The diagram below shows the organization of L2 container partition for GPT.
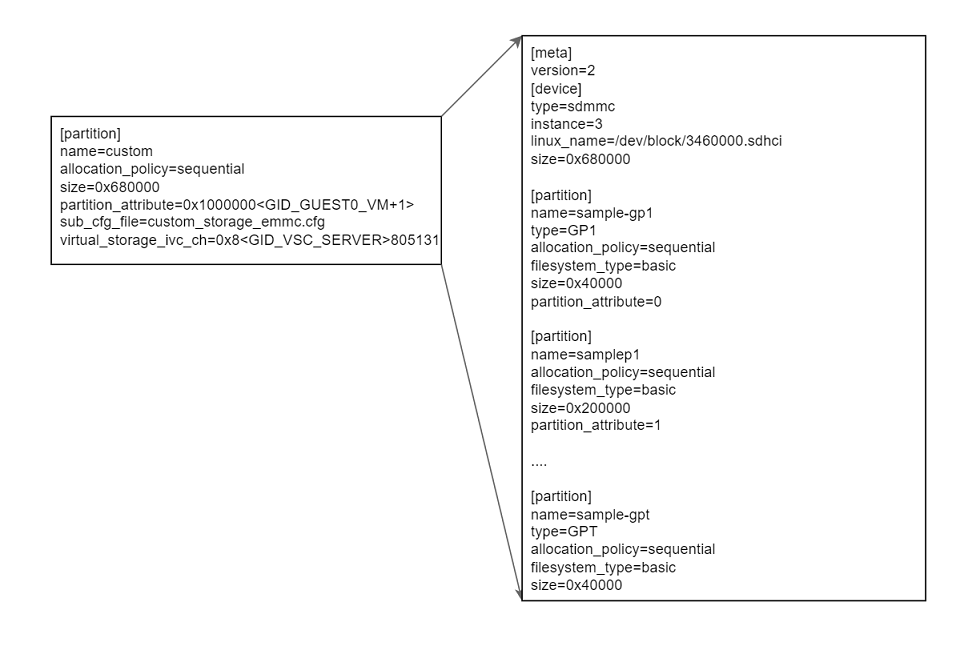
Multiple GPT partitions can be added for the same guest. The GPT primary and secondary are generated by using the container partition name as prefix.
Example Changes for Both Linux and QNX GOS VM
Configuration files are in the following folder:
<top>/<NV_SDK_NAME_FOUNDATION>/platform-config/hardware/nvidia/platform/t23x/automotive/pct/drive_av/<PCT>Where:
<PCT>is qnx or dual-qnx or linux.
The following example snippet shows changes required to add custom partition in L2:
boot_chain_storage.cfg
[device]
type=sdmmc
instance=3
linux_name=/dev/block/3460000.sdhci
size=EMMC_BOOTCHAIN_SIZE
...
[partition]
name=custom
allocation_policy=sequential
size=0x680000
partition_attribute=0x1000000<GID_GUEST0_VM+1>
sub_cfg_file=custom_storage_emmc.cfg
virtual_storage_ivc_ch=0x8<GID_VSC_SERVER>805131Note:
IVC Channel(0x31=49) and Mempool(0x51=81) used in virtual_storage_ivc_ch are subject to availability.
Refer to platform_config.h and platform_ivc_config.h for available IVC/Mempool Ids.
Note:
partition_attribute is described in
"Mass Storage Partition Configuration / Customizing the Configuration File / Setting Attributes / Partition Attributes Table" of NVIDIA DRIVE OS 6.0 Linux SDK Developer Guide.
or
"Storage / Mass Storage Partition Configuration / Customizing the Configuration File / Setting Attributes / Partition Attributes Table" of NVIDIA DRIVE OS 6.0 QNX SDK Developer Guide.
The next step is to add IVC and mempool entry in the platform_config.h file for custom partition.
IVC entry:
[49] = { .peers = {GID_GUEST0_VM, GID_VSC_SERVER}, .nframes = 1, .frame_size = 128 },Mempool entry:
[81] = { .peers = {GID_GUEST0_VM, GID_VSC_SERVER}, .size = (SZ_1MB * 8), .align = (SZ_1MB * 2) },More custom partitions can be added with the same guest ID in the partition_attribute. The container partition name is used to differentiate between multiple GPT partition tables for the same guest.
For the example above the GPT is defined within the sub config file "custom_storage_emmc.cfg".
The following shows an example of how to define GPT L3 partitions.
custom_storage_emmc.cfg
[meta]
version=2
[device]
type=sdmmc
instance=3
linux_name=/dev/block/3460000.sdhci
size=0x680000
[partition]
name=sample-gp1
type=GP1
allocation_policy=sequential
filesystem_type=basic
size=0x40000
partition_attribute=0
[partition]
name=samplep1
allocation_policy=sequential
filesystem_type=basic
size=0x200000
partition_attribute=1
[partition]
name=samplep2
allocation_policy=sequential
filesystem_type=basic
size=0x200000
partition_attribute=1
[partition]
name=samplep3
allocation_policy=sequential
filesystem_type=basic
size=0x200000
partition_attribute=1
[partition]
name=sample-gpt
type=GPT
allocation_policy=sequential
filesystem_type=basic
size=0x40000Example Changes for QNX GOS VM
Add device tree entry to let QNX enumerate each of the partitions inside the container as virtual block devices, as in the following example:
<top>/<NV_SDK_NAME_QNX>/bsp/device-tree/hardware/nvidia/platform/t23x/automotive/kernel-dts/common/qnx/storage/tegra234-common-driveav-storage-gos0.dtsi
tegra_virt_storage32 {
compatible = "nvidia,tegra-hv-storage";
status = "okay";
instance = <10>;
ivc = <&tegra_hv 49>;
mempool = <81>;
device-type = "vblk_mnand";
partition-name = "custom";
};
NOTE: Ensure tegra_virt_storage32 is unique in the above mentioned dtsi file.
Pick a different instance of tegra_virt_storage, if tegra_virt_storage32 is already in use.Add the nvsciipc table entry in the
<top>/<NV_SDK_NAME_QNX>/bsp/device-tree/hardware/nvidia/platform/t23x/automotive/kernel-dts/common/qnx/tegra234-nvsciipc-gos0.dtsi
"INTER_VM", "nvhvblk_49", "49", "0", /* nvhvblk_guest */Example Changes for Linux GOS VM
Add device tree entry to let Linux enumerate each of the partitions inside the container as virtual block devices, as in the following example:
<top>/<NV_SDK_NAME_LINUX>/kernel/source/hardware/nvidia/platform/t23x/automotive/kernel-dts/common/linux/storage/tegra234-common-storage-linux-gos.dtsi
tegra_virt_storage32 {
compatible = "nvidia,tegra-hv-storage";
status = "okay";
instance = <40>;
ivc = <&tegra_hv 49>;
mempool = <81>;
};
NOTE: Ensure tegra_virt_storage32 is unique in the above mentioned dtsi file.
Pick a different instance of tegra_virt_storage, if tegra_virt_storage32 is already in use.Caution and Verification
The size of the device at L3 matches the size of the extended custom partition at L2:
The custom container has three partitions each of 2MB. Note that the filename is not specified above. If file is not specified, flash tools will not create any images for these partitions but the space is allocated and will be formatted if specified. If an image is required, update the partition within the custom cfg file accordingly to add the filename field and point it to the file you want to flash.
Once booted with upper changes, the GPT partitions are enumerated as virtual block devices in each Guest OS(QNX or Linux).
For QNX, for example, if the container block device is enumerated as /dev/vblk_mnanda0, then the individual partitions are /dev/vblk_mnanda0.ms.0, /dev/vblk_mnanda0.ms.1, and /dev/vblk_mnanda0.ms.2.
For Linux, if the container block device is enumerated as /dev/vblkdev40, then the individual partitions are /dev/vblkdev40p1, /dev/vblkdev40p2, and /dev/vblkdev40p3.
QNX FS Images
The GPT partitions added above do not have a file image associated, so create_bsp_images does not generate images for these partitions. Follow the steps below to create a qnx6 dummy fs image with some contents.
1.Create an empty folder mkdir custom_fs.
2.Create some text files using touch, and add some content to the custom_fs folder.
3.Create the qnx_rootfs_build file with the contents and save as qnx_rootfs_build:
[num_sectors=4096]
[-followlink]
[perms=0755 dperms=0755 uid=0 gid=0] /=./custom_fs
[type=link]/tmp=/dev/shmem4.Make sure that QNX_TARGET and QNX_HOST paths are set correctly.
$QNX_HOST/usr/bin/mkxfs -t qnx6fsimg qnx_rootfs_build custom_qnxfs.img=====================================
Glossary
PCT: Partition Configuration Table.
AV: Autonomous Vehicle.
VM: Virtual machine.
IVC: Inter-Virtual machine Channel
mempool: Shared buffer implementation between two VMs
VSC: Virtual Storage Controller