Platform Software Stacks
This section describes the platform component software stacks.
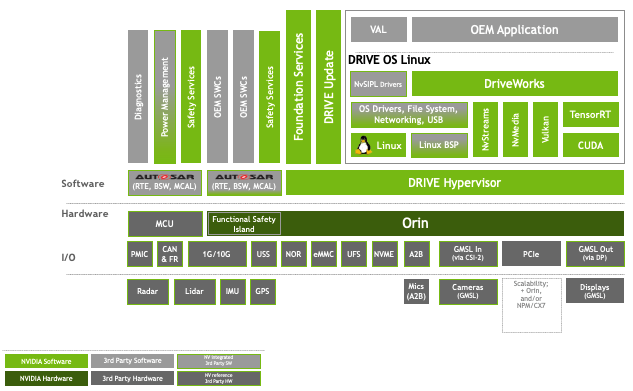
Use the DRIVE OS software stack to build your autonomous vehicle applications.
Foundation Services Stack
The NVIDIA DRIVE AGX? platform Foundation services runtime software stack provides the infrastructure for all the components of the platform. With this infrastructure, guest OS systems can run on the hardware, with the Hypervisor managing use of hardware resources.
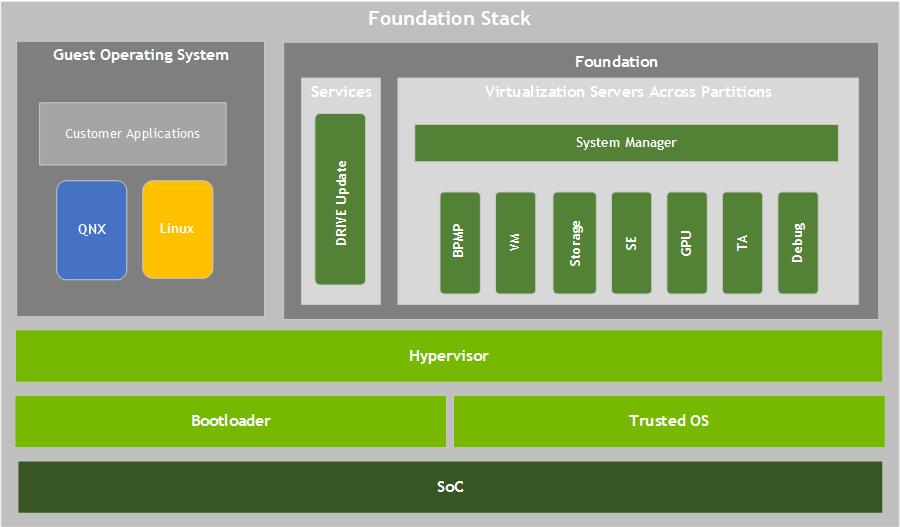
Foundation Components
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Hypervisor |
Trusted Software server that separates the system into partitions. Each partition can contain an operating system or a bare-metal application. The Hypervisor manages:
Hypervisor is optimized to run on the ARMv8.2 Architecture. |
| guest OS |
Allocates peripherals that Guest OS needs to control. |
| Services |
Services for DRIVE Update. |
| Bootloader |
Firmware that runs during boot to load firmware components, such as boot images, partition images, and other firmware. |
| Trusted OS |
Trusted OS configuration in the PCT describes the configuration of the virtual Trusted OS device. |
| Orin SoC |
System on a Chip hardware resources. |
Virtualized Servers
The virtualized configurable servers are as follows.
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Boot and Power Manager Processor (BPMP) Server |
Facilitates communication between Guest Virtual Machines (VM) and BPMP firmware. |
| VM Server |
host1X virtualizes NvHost. |
| Security Engine (SE) Server |
Para-virtualizes and allows multiple Guest Virtual Machines access to the security engine cryptographic hardware accelerator. |
| Trusted Applications (TA) |
Through Trusted Applications, Trusted OS exposes a set of core services that use managed security assets in cryptographic operations without exposing them to non-secure guest software. |
| GPU |
Runs on top of the virtualization core and handles sharing of GPU between multiple client Guest Virtual Machines. The GPU virtualization also includes the para-virtualized GPU client driver running inside of each Guest Virtual Machine. |
| Storage Server |
Para-virtualizes storage access to enable sharing physical storage devices among multiple Guest Virtual Machines. |
| Debug Server | Provides support for kernel-level debugging of Guest Virtual Machines (VM). |
NvMedia Architecture
NvMedia provides powerful processing of multimedia data for true hardware acceleration across NVIDIA DRIVE? Orin? devices. With the NvMedia and Orin firmware components, multimedia applications support multiple simultaneous camera feeds for simultaneous processing. The NvMedia features include:
- Robust image processing and sensor control blocks for use by applications.
- Hardware surface to handle all types of image formats such as RGB, YUV and RAW.
- Functional components for image capture, processing, acceleration, encoding, and interoperating with other libraries.
Applications leverage the NvMedia Application Programming Interface (API) to process image and video data. Additionally, NvMedia can route image data to/from other components, such as OpenGL ES and NVIDIA? CUDA?.
NvMedia Stack
The NvMedia software stack supports these types of interactions:
- Applications call the NvMedia Framework components to string together a sequence of processing steps for images.
- The NvMedia Framework calls low-level hardware drivers to interact with the SoC components on the SoC chip.
Consult building and running NvMedia sample applications to build an NvMedia sample application.
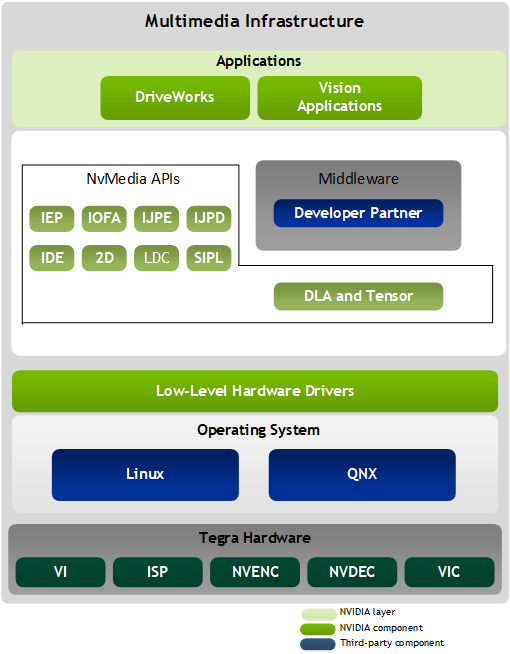
Each component functionality is as follows. The drivers expose a subset of the functionality available.
|
Tegra Hardware |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Video Input (VI) |
Receives CSI data from the camera. |
|
Image Signal Processor (ISP) |
Produces a processed image from image data captured from an image sensor. For example, it can make pixel-level changes such as inverting pixel bits, auto exposure, and white balance correction. |
|
NVIDIA Encoder (NVENC) |
Converts raw image data into one of the supported image formats. |
|
NVIDIA Decoder (NVDEC) |
Converts encoded image data into raw image data. |
|
Video Interlace Compositor (VIC) |
Converts video data for deinterlacing, composition, and format conversion. |
|
Optical Flow Accelerator (OFA) |
Accelerate optical flow and stereo disparity computation between the frames. |
NvMedia Components
The NvMedia components are as follows:
|
Image Component |
Description |
|---|---|
|
SIPL |
The SIPL framework processes incoming image data with AE, AWB controls and includes the ISP processing capability. It supports camera tuning tools. |
|
2D |
Image 2D provides the ability to perform manipulation of image data; such as cropping, scaling, copying, and converting the format. |
|
IEP |
Image Encode Processing provides the ability to encode processed YCRCb surface inputs to H.264 and H.265. |
|
IJE |
Image JPEG Encoding provides the ability to encode YUV surfaces to JPEG format. |
|
IJD |
Image JPEG Decoding provides the ability to decode images compressed inJPEG format to raw YUV surfaces. |
NvMedia APIs and Thread Safety
NvMedia APIs are not designed to be thread safe. It is the responsibility of the application to maintain thread safety. To ensure thread safety:
- NvMedia components can be created and used in any thread but the APIs cannot be used from different threads concurrently.
- Different instances of the same component can be used in parallel from different threads.
- Encoders are designed to be fed from one thread and get the encoded bitstream from another thread.